Hepatitis infection (A B C)
Could there be something more going on with your flu-like symptoms than a common virus?
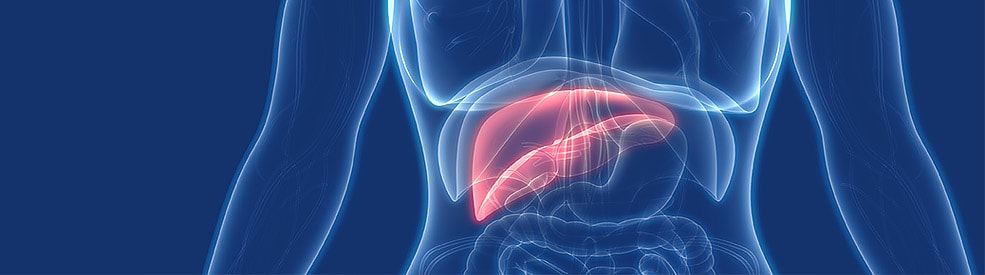
Hepatitis infection, an inflammation of the liver, can be detected by vague complaints of feeling unwell, fever, muscle aches, and loss of appetite.
The chronic form of certain hepatitis can result in severe liver damage, cirrhosis (a potentially fatal scarring condition), liver cancer, and liver failure.
Although there are many causes of hepatitis infection, hepatitis A, B, or C infections are typically to blame in the Nigeria.
Hepatitis A infection
Can hepatitis A virus is commonly transmitted? Yes! When an infected person neglects to wash his or her hands after using the toilet and then handles the food you eat. The liver usually heals completely within one to two months in most people.
Hepatitis A vaccine is advised for:
All children
People with liver disease
Day-care workers
Household members of infected people
International travelers
What is Hepatitis B infection?
Because it is a viral disease, Hepatitis B virus is spread through contact with the blood, saliva, semen or vaginal secretions of infected people. Pregnant women should be tested for hepatitis B because their babies can become infected during childbirth.
The infection usually resolves within six months for most adults, at which point most people develop immunity to the virus. Treatment for chronic hepatitis B infection may include medications and ongoing monitoring of liver health.
Hepatitis B vaccine is advised for:
All infants and children
Hemodialysis patients
People with liver disease
International travelers
Health care, emergency or correctional facility workers
Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus can lead to acute or chronic infection of the liver.
“It’s the most common type of chronic hepatitis found in the Nigeria and is spread through direct exposure to infected blood,”
While no vaccine exists for hepatitis C, acute and chronic types of the illness can be cured with the use of direct-acting antiviral agents prescribed by your doctor.
Your doctor may recommend hepatitis C testing if you:
Were born between 1945 and 1965
Had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
Received clotting factors (used by hemophiliacs) before 1987
Had/have tattoos or body piercings
Used/use injected drugs and shared needles
Symptoms of an infection infection
The illnesses share some common symptoms, including:
Fatigue
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhea
Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes
Abdominal pain or discomfort
Dark-colored urine or light-colored bowel movements
Hepatitis does not always cause symptoms.
How to prevent hepatitis
Take these steps to protect yourself and your family against hepatitis infection:
If you think you’ve been exposed to hepatitis, see your doctor right away. Receiving immune globulin and vaccinations may thwart infection
Be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
Wash your hands before preparing and eating food, and after using the bathroom and changing diapers
Don’t eat raw shellfish
Avoid sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes and razors
Don’t share or reuse hypodermic needles
As a pregnant woman, get tested for hepatitis viruses
Before getting a tattoo or body piercing, be sure the facility is licensed and meets all health and safety requirements
Avoid unprotected sex with an infected partner

Leave a Reply